Understanding Compliance Regulations for Powder Pouch Filling
The powder pouch filling industry is subject to a myriad of compliance regulations to ensure the safety and quality of products. Understanding these regulations is crucial for manufacturers to maintain compliance and avoid costly penalties.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs)
GMPs are the cornerstone of compliance for powder pouch filling operations. They establish standards for manufacturing, packaging, and storage to minimize contamination and ensure product quality. GMPs cover aspects such as:
– Sanitation and Hygiene: Maintaining a clean and hygienic environment, including regular cleaning and disinfection of equipment and surfaces.
– Personnel Training: Ensuring that personnel are trained on GMPs and proper handling techniques.
– Equipment Validation: Verifying that equipment meets specifications and is suitable for the intended purpose.
– Product Testing and Control: Conducting in-process and finished product testing to ensure compliance with quality standards.
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP)
HACCP is a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and controlling hazards that could compromise product safety. In powder pouch filling, HACCP focuses on critical control points (CCPs) where contamination or quality issues can occur.
– Hazard Identification: Identifying potential hazards, such as microbial contamination, physical contaminants, and chemical residues.
– Critical Control Point (CCP) Determination: Determining the points in the process where hazards can be prevented or eliminated.
– Critical Limit Setting: Establishing acceptable limits for CCPs to ensure that hazards are controlled.
– Monitoring and Corrective Action: Regularly monitoring CCPs and taking corrective actions when limits are exceeded.
Allergen Management
Allergens, such as peanuts, tree nuts, and dairy, pose significant health risks to consumers. Compliance regulations require manufacturers to implement allergen management programs to prevent cross-contamination.
– Allergen Identification: Identifying and labeling ingredients that contain allergens.
– Separation and Control: Physically separating allergen-containing materials from other products.
– Cleaning and Sanitation: Rigorously cleaning and disinfecting equipment and surfaces to prevent allergen carryover.
– Documentation and Traceability: Maintaining records of allergen handling and traceability throughout the supply chain.
Packaging and Labeling Regulations
Packaging and labeling regulations ensure that powder pouches provide consumers with accurate and necessary information. Regulations cover:
– Material Specification: Adhering to specific material requirements for pouches to maintain product integrity.
– Labeling Requirements: Including essential information on labels, such as product name, ingredients, nutrition facts, and storage instructions.
– Child-Resistant Packaging: Implementing child-resistant packaging for certain products to prevent accidental ingestion.
Regulatory Authorities
Understanding compliance regulations also involves familiarity with regulatory authorities responsible for enforcement. Key authorities include:
– U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Oversees food and drug safety in the United States.
– European Food Safety Authority (EFSA): Responsible for food safety in the European Union.
– Health Canada: Regulates food and drug products in Canada.
– Other national and international agencies: Enforce compliance with regulations in their respective jurisdictions.
By adhering to compliance regulations, powder pouch filling manufacturers can ensure product safety, protect consumers, and maintain regulatory compliance. Understanding the requirements and implementing effective compliance programs is essential for successful and sustainable operations.
-

Advanced Packing Solutions: Snacks, Sugar, and Frozen Food Machines
29-10-2025 -

Efficient and Reliable Solutions for Salt, Nuts, and Frozen Dumplings Packing
29-10-2025 -

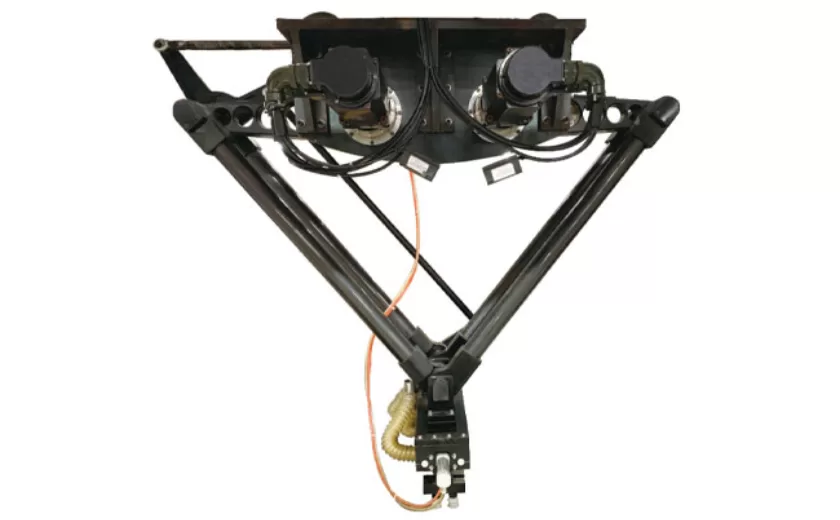
High-Performance Biscuits, Lollipop, and Ketchup Packing Machines for Modern Food Production
29-10-2025 -

Efficient Liquid Filling and Packing Machines for Modern Production
23-10-2025 -

Reliable Granule Packaging Machines for Efficient Production
23-10-2025 -

Efficient Auger Powder Filling Machines for Accurate Packaging
23-10-2025 -

High-Performance Liquid Filling and Packing Machines for Hygienic Production
10-10-2025 -

High-Efficiency Granule Packaging Machines for Precision and Speed
10-10-2025 -

High-Precision Auger Type Powder Filling Machines for Efficient Packaging
10-10-2025 -

Efficient Vertical Form Fill Seal Packaging Machines for Smart Production
10-10-2025