The Science Behind Liquid Sachet Packaging
Introduction:
The world of packaging has seen a significant shift towards liquid sachets, offering a convenient and portable solution for storing and distributing various liquids. From beverages to condiments and personal care products, these individual sachets have become ubiquitous in our daily lives. However, beyond their practical applications lies a fascinating realm of scientific principles and materials engineering that enables them to perform their unique functions. This article delves into the science behind liquid sachet packaging, exploring the intricacies of materials, barrier properties, and manufacturing processes.
Material Composition
Liquid sachets are primarily composed of flexible polymers, such as polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP). These materials are chosen for their strength, flexibility, and ability to withstand the contents without degradation. They also provide a lightweight and cost-effective alternative to traditional rigid containers.
Within these polymers, additional layers can be incorporated to enhance specific properties. For example, a metallized layer can be added to block light and oxygen, providing extended shelf life for sensitive liquids. Aluminum foil, with its excellent barrier properties against moisture and gases, can also be used for products that require higher levels of protection.
Barrier Properties
The key to preserving the quality and freshness of liquids within sachets lies in their barrier properties. Sachets are engineered with multiple layers that prevent the ingress of oxygen, moisture, light, and other contaminants.
Oxygen and moisture are primary culprits in product spoilage and deterioration. The polymer layers in sachets act as a barrier against these elements, preventing their interaction with the liquid contents. Aluminum foil and metallized layers further enhance these barrier properties, creating an almost impermeable seal.
Sterilization and Hygiene
To ensure the safety and quality of the liquids contained within, sachets undergo rigorous sterilization processes. This includes exposing the materials to heat or radiation to kill any potential microorganisms.
The sterilization process also contributes to the barrier properties of the sachets. By eliminating microorganisms, the risk of internal contamination is minimized, ensuring the product’s longevity and purity.
Filling and Sealing Technology
The success of liquid sachets depends on the precision and efficiency of the filling and sealing processes. Advanced machinery is employed to accurately dispense the desired amount of liquid into each sachet. This is crucial for consistency and quality control.
Sachets are then sealed using heat or ultrasonic welding techniques. These methods create a hermetic seal that prevents leakage and maintains the integrity of the contents. The seals are inspected for strength and durability to ensure that the sachets meet the highest standards of packaging.
:
The science behind liquid sachet packaging is a complex but fascinating field that involves multiple disciplines, from materials science to manufacturing processes. Through careful selection of polymers, incorporation of barrier layers, rigorous sterilization, and precise filling and sealing, liquid sachets provide a safe, convenient, and cost-effective solution for a wide range of products. Their scientific underpinnings ensure the preservation of liquid quality, freshness, and hygiene, making them an indispensable part of our modern lives.
-

Advanced Packing Solutions: Snacks, Sugar, and Frozen Food Machines
29-10-2025 -

Efficient and Reliable Solutions for Salt, Nuts, and Frozen Dumplings Packing
29-10-2025 -

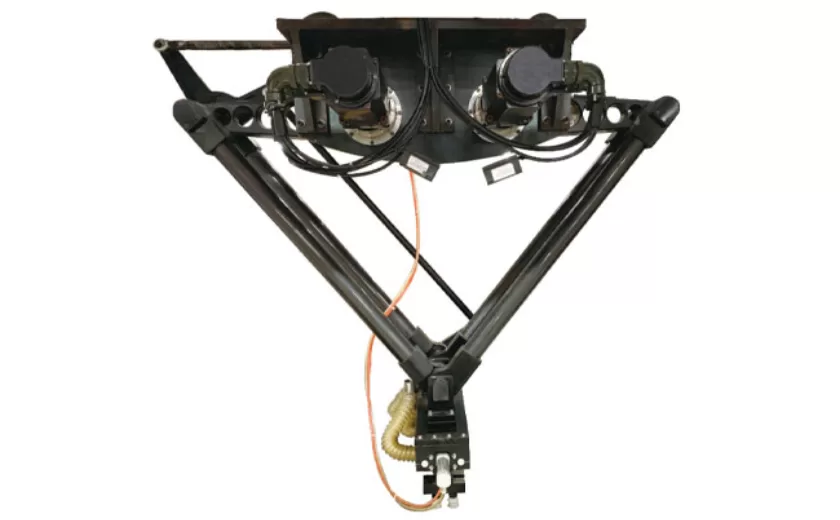
High-Performance Biscuits, Lollipop, and Ketchup Packing Machines for Modern Food Production
29-10-2025 -

Efficient Liquid Filling and Packing Machines for Modern Production
23-10-2025 -

Reliable Granule Packaging Machines for Efficient Production
23-10-2025 -

Efficient Auger Powder Filling Machines for Accurate Packaging
23-10-2025 -

High-Performance Liquid Filling and Packing Machines for Hygienic Production
10-10-2025 -

High-Efficiency Granule Packaging Machines for Precision and Speed
10-10-2025 -

High-Precision Auger Type Powder Filling Machines for Efficient Packaging
10-10-2025 -

Efficient Vertical Form Fill Seal Packaging Machines for Smart Production
10-10-2025