Best Practices for Maintaining Hygiene in Juice Filling Operations
Maintaining impeccable hygiene in juice filling operations is paramount to ensure the safety, quality, and shelf life of the final product. By adhering to best practices, manufacturers can minimize the risk of contamination and guarantee the production of wholesome and nutritious juices.
Prerequisite Programs
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs): Establish a comprehensive framework for hygiene and sanitation practices, covering all aspects of the operation from product design to packaging.
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP): Identify potential hazards in the filling process and implement preventive measures to control and eliminate them.
Environmental Controls
Facility Design: Design facilities to facilitate easy cleaning and prevent the accumulation of debris. Use smooth, non-porous surfaces and avoid crevices that can harbor bacteria.
Air Quality: Control air quality to minimize the risk of airborne contamination. Use HEPA filters and maintain positive air pressure in critical areas.
Water Quality: Use potable water for all cleaning and rinsing operations. Regularly monitor water quality to ensure compliance with standards.
Employee Hygiene
Personal Hygiene: Train employees on the importance of personal hygiene and provide appropriate facilities for handwashing, sanitizing, and changing into clean uniforms.
Health Monitoring: Implement health monitoring programs to detect and manage potential sources of contamination. Consider regular medical examinations and exclusion policies for employees with illnesses.
Equipment and Process Hygiene
Sanitation Protocols: Develop and implement thorough sanitation protocols for all equipment and surfaces that come into contact with juice. Use approved cleaning and sanitizing agents and follow manufacturer’s instructions.
Cleaning and Maintenance: Regularly clean and maintain equipment to prevent the build-up of debris and biofilms. Use appropriate cleaning tools and chemicals to ensure effective removal of contaminants.
Product Handling: Utilize automated systems and closed processing to minimize human intervention and reduce the risk of contamination during product handling.
Monitoring and Corrective Actions
Microbial Monitoring: Regularly monitor the environment, equipment, and finished product for the presence of microorganisms. Use appropriate testing methods and establish action limits.
Corrective Actions: Promptly investigate and address any deviations from established hygiene standards. Implement corrective actions to eliminate identified hazards and prevent recurrence.
Continuous Improvement
Regular Audits: Conduct regular internal audits to assess compliance with hygiene best practices and identify areas for improvement.
Training and Education: Train employees on hygiene principles and refresher training to reinforce best practices.
By adhering to these best practices, juice filling operations can establish a robust and effective hygiene program that minimizes the risk of contamination and ensures the production of safe, high-quality juice products.
-

Auger Type Powder Filling Machine: The Ultimate Guide to Precision Packaging
09-03-2026 -

Advanced Packing Solutions: Snacks, Sugar, and Frozen Food Machines
29-10-2025 -

Efficient and Reliable Solutions for Salt, Nuts, and Frozen Dumplings Packing
29-10-2025 -
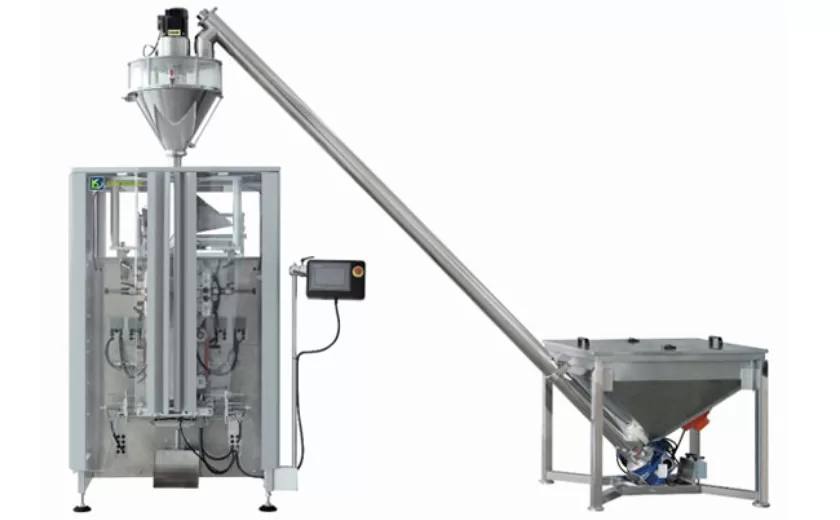

High-Performance Biscuits, Lollipop, and Ketchup Packing Machines for Modern Food Production
29-10-2025 -

Efficient Liquid Filling and Packing Machines for Modern Production
23-10-2025 -
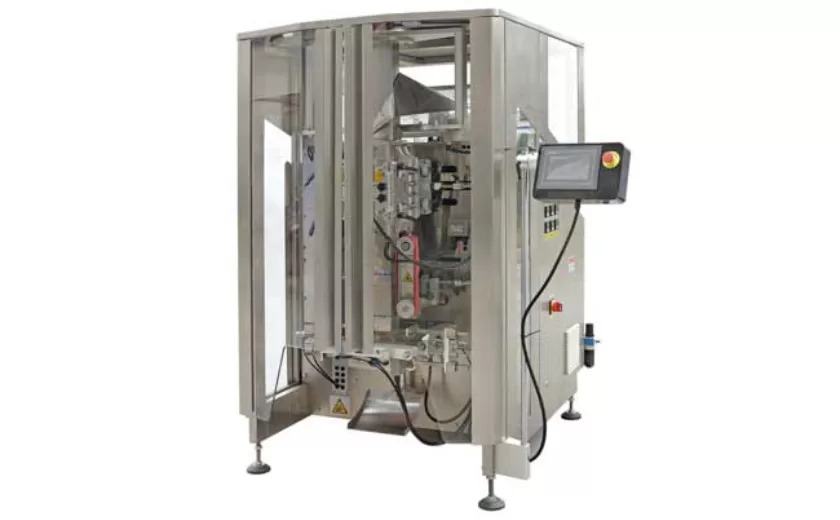

Reliable Granule Packaging Machines for Efficient Production
23-10-2025 -

Efficient Auger Powder Filling Machines for Accurate Packaging
23-10-2025 -

High-Performance Liquid Filling and Packing Machines for Hygienic Production
10-10-2025 -

High-Efficiency Granule Packaging Machines for Precision and Speed
10-10-2025 -

High-Precision Auger Type Powder Filling Machines for Efficient Packaging
10-10-2025