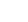
Package Diagram for Banking System
Package Diagram for Banking System
In the realm of modern-day banking systems, the intricate nature of operations necessitates a well-thought-out architectural design. One such design tool that plays a pivotal role is the package diagram. A package diagram illustrates the organization and arrangement of elements in a system, showcasing how various components interact and function together within distinct packages.
When considering a banking system, the need for meticulous planning and structuring is undeniable. Let’s delve into the components typically found in a package diagram for a banking system:
- Banking System Package: This top-level package encapsulates the entire banking system and serves as the entry point for all functionalities.
- Customer Management: This package encompasses modules related to customer onboarding, profiles, and account management.
- Transactions: Here, functionalities related to deposits, withdrawals, transfers, and payments find their place, ensuring seamless financial transactions for customers.
- Security: Security is paramount in banking systems; this package includes features like authentication, authorization, and encryption mechanisms.
- Reporting: Reporting functionalities fall under this package, enabling the generation of statements, analytics, and regulatory reports.
- Integration: Integration packages cater to connecting the banking system with external services, such as payment gateways and credit bureaus.
As we can see, a well-organized package diagram provides a holistic view of the banking system’s architecture, facilitating better understanding and maintenance of the system.
The Importance of Package Diagrams in Banking Systems
Package diagrams serve as a visual aid that aids in comprehending the structure, dependencies, and interactions within a banking system. Here are a few key reasons why package diagrams are crucial:
- Modularity: By organizing functionalities into packages, the system becomes modular, allowing for easier modifications and updates without affecting the entire system.
- Clarity: With a clear visual representation, stakeholders can quickly grasp the system’s architecture and functionalities, enhancing communication and collaboration.
- Scalability: Package diagrams lay the foundation for scalability, enabling the system to grow and accommodate new features or changes seamlessly.
- Maintainability: Understanding the system’s structure through package diagrams simplifies maintenance tasks, reducing complexity and enhancing system stability.
- Documentation: Package diagrams serve as valuable documentation, aiding developers, testers, and other stakeholders in understanding the system’s design and functionality.
Evolution of Banking System Architectures
The evolution of package diagrams in banking systems mirrors the advancements in technology and the growing complexity of financial services. Traditional banking systems were characterized by monolithic architectures where all functionalities were tightly integrated.
However, with the advent of microservices and modular architectures, modern banking systems have embraced a more decentralized approach. Package diagrams now reflect this shift, emphasizing the segregation of functionalities into distinct modules or packages.
Furthermore, the rise of cloud-based solutions and APIs has reshaped the way banking systems are designed and interconnected. Package diagrams play a crucial role in illustrating how these components interact and communicate, ensuring seamless operations and enhanced scalability.
Innovations in Banking System Design
Recent innovations in banking system design have focused on enhancing user experiences, improving security measures, and streamlining operations. Package diagrams have adapted to incorporate these innovations, showcasing how features like biometric authentication, AI-driven analytics, and real-time transaction monitoring fit within the system’s architecture.
Furthermore, the integration of blockchain technology and decentralized finance (DeFi) principles has presented new challenges and opportunities for banking system designs. Package diagrams now include components related to smart contracts, decentralized ledgers, and interoperability with blockchain networks.
Conclusion
Package diagrams play a pivotal role in structuring, visualizing, and understanding the complexities of modern banking systems. By encapsulating functionalities into coherent packages, these diagrams provide a roadmap for architects, developers, and stakeholders to navigate the intricate landscape of banking system design.
As technology continues to evolve and consumer expectations shift, package diagrams will remain a fundamental tool in shaping the future of banking system architectures, ensuring robustness, scalability, and innovation in the ever-changing financial landscape.
-

Advanced Packing Solutions: Snacks, Sugar, and Frozen Food Machines
29-10-2025 -

Efficient and Reliable Solutions for Salt, Nuts, and Frozen Dumplings Packing
29-10-2025 -

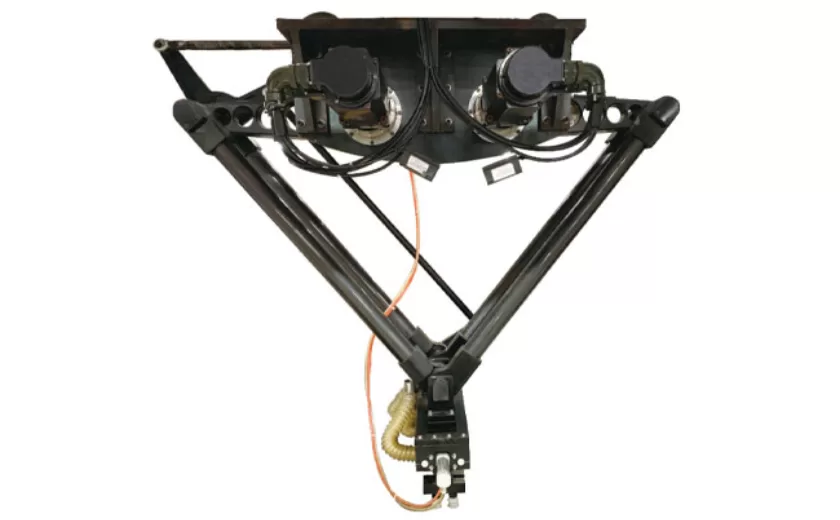
High-Performance Biscuits, Lollipop, and Ketchup Packing Machines for Modern Food Production
29-10-2025 -

Efficient Liquid Filling and Packing Machines for Modern Production
23-10-2025 -

Reliable Granule Packaging Machines for Efficient Production
23-10-2025 -

Efficient Auger Powder Filling Machines for Accurate Packaging
23-10-2025 -

High-Performance Liquid Filling and Packing Machines for Hygienic Production
10-10-2025 -

High-Efficiency Granule Packaging Machines for Precision and Speed
10-10-2025 -

High-Precision Auger Type Powder Filling Machines for Efficient Packaging
10-10-2025 -

Efficient Vertical Form Fill Seal Packaging Machines for Smart Production
10-10-2025